A Peculiar Case of a Floating Angio-Seal
Abstract
Purpose
To show a complication of the use of an Angio-Seal™ closure device.
Case
We present a patient with a systolic murmur in his femoral artery after PCI. The murmur was caused by a dislocated Angio-Seal™, a vascular closure device. This was diagnosed by Doppler Ultrasound. The device was surgically removed.
Conclusion
Vascular complications, such as lower limb ischemia, requiring surgical intervention tend to be higher after use of a vascular closure device. We advise routine physical examination of the puncture site after percutaneous closure with a vascular closure device, such as an Angio-Seal™. The removal of the device can be performed via an open or endoscopic approach, based on available experience.
INTRODUCTION
In this case we describe a complication caused by a dislocated Angio-Seal™ device after percutaneous intervention and how we approached this problem. We also provide a brief overview of the literature regarding this complication and possible solutions.
CASE
A 63-year-old man had been subjected to a percutaneous coronary intervention via his right femoral artery. At the end of the uncomplicated procedure, the puncture site was closed using an Angio-Seal™ (St Jude Medical, Minnesota, USA). The patient had no post-interventional complaints of pain in his lower limb and there were no signs of limb ischemia. Routine physical examination of the puncture site revealed a systolic murmur over his right femoral artery. An arterial Doppler ultrasound was made, which showed a mobile structure floating in the common femoral artery (Fig. 1, video 1). It was hypothesized that the Angio-Seal™ had dislocated after the procedure and was now floating in the common femoral artery. Considering the risk of arterial thrombosis or dislodgement and thereby possibly embolization to the popliteal or crural arteries, there was an indication for surgical removal of the Angio-Seal™. After adequate exposure and vascular control of the common femoral artery, superficial and deep femoral artery, a longitudinal incision was made in the common and superficial femoral artery and the Angio-Seal™ was removed entirely (Fig. 2). The longitudinal incision was closed primary with prolene stitches, taking care that no stenosis occurred. A postoperative Doppler ultrasound showed no stenosis and a normal flow pattern. The patient was discharged without any clinical
symptoms or complications on the second postoperative day. Patient consent was obtained for publishing this case.
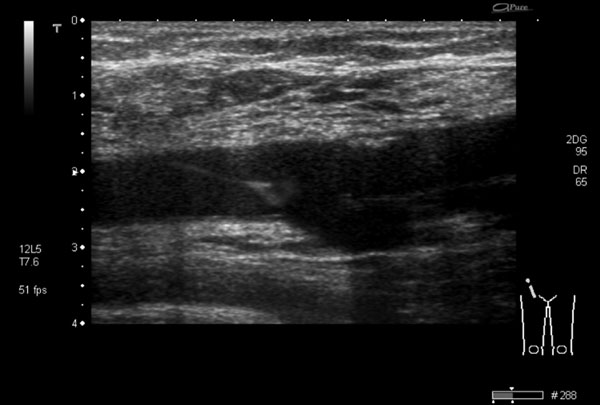
Ultrasound of the common femoral artery, showing the luxated anchor of the Angio-Seal™, floating in the lumen, hanging on the suture from the vessel wall.
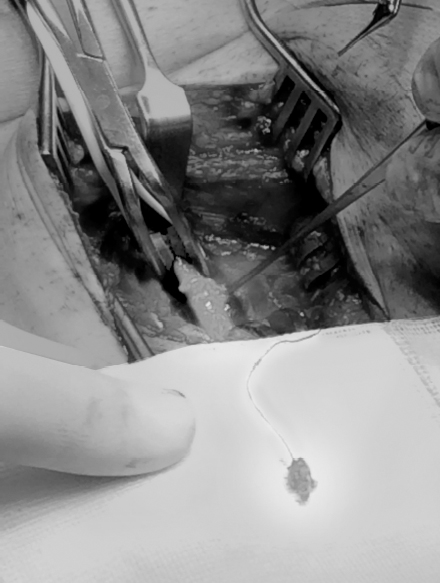

The Angio-Seal™ was surgically removed through a vertical incision of the common femoral artery.
DISCUSSION
An Angio-Seal™ is a bio-absorbable arterial closure device that is placed after a percutaneous intervention to achieve haemostasis and prevent extra-luminal bleeding. The aim of this device is earlier mobilisation, which reduces hospital admission duration and consequently, medical costs. It consists of three parts; an intra-arterial bio-absorbable anchor, a suture and an extra-arterial collagen sponge to seal the vessel. The sponge should be pushed over the suture to attain compression to the outside of the arterial wall, thereby pulling the intraluminal anchor to the inside of the vessel wall in order to fully close the puncture hole. The anchor and suture completely dissolve within 90 days [5]. In this specific case, the collagen sponge was probably not pressed firmly enough to the outer arterial wall during Angio-Seal™ placement, enabling the anchor to luxate and float in the common femoral artery (Fig. 1). The suture on the anchor prevented dislodgement of the anchor and consequent symptoms of limb ischemia.
A literature search was conducted to identify common complications of the use of vascular closure devices, such as an Angio-Seal. Complications that were most frequently encountered included groin bleeding, arterial stenosis and infection [1]. A large meta-analysis [1] comparing vascular closure devices with manual or mechanic compression after coronary angiography or percutaneous intervention showed that lower limb ischemia and other ischemic arterial complications (0.3% versus 0.0%, p=0.07), the need of surgery for vascular complications (0.7% versus 0.4%, p=0.10) and the risk of groin infection (0.6% versus 0.2%, p=0.02) tended to be higher in the vascular closure device groups. For Angio-Seal patients only, the risk of arterial stenosis, limb ischemia or device luxation was comparable to patients with manual or mechanic compression (RR 3.00, 95% CI 0.12-73.35). The risk of arterial complications that required vascular surgery was also not significantly higher in the intervention-group using an Angio-Seal™ (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.17-5.74).
There are several techniques to remove a luxated vascular closure device[2-4]. Recently, Boersma et al. [4] described a case in which a luxated Angio-seal™ was removed with an endovascular Alligator Tooth Retrieval Forceps in the distal femoral artery. Two other cases describe patients who needed vascular surgery to remove the luxated device similar to the case described in this article [2, 3]. We chose a surgical approach because of the risk of distal embolization and lack of experience in removing a luxated Angio-Seal™ with an endovascular technique.
CONCLUSION
Dislocation of an Angio-Seal™ closure device is a rare complication, which normally requires an intervention to prevent embolism, arterial thrombosis or limb ischemia. The removal of the device can be performed via an open or endoscopic technique, based on available experience and preference. Physicians using an Angio-Seal™ should be aware that inadequate pressure of the Angio-Seal™ firmly to the vessel wall could potentially result in its potential dislocation. Current manuscript displays distinctive ultrasound imaging of the floating Angio-Seal™ in the common femoral artery. We advise routine physical examination of the puncture site after percutaneous closure to assess presence of a systolic murmur prior to discharge.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Video 1. Ultrasound of the common femoral artery, showing the luxated anchor of the Angio-Seal™, floating in the lumen, hanging on the suture from the vessel wall.


